Urinary incontinence and genital prolapse
Home » Female Functional Unit » Urinary Incontinence and Genital Prolapse

Urinary incontinence is defined as any involuntary urination and is a medical, social and hygienic problem that significantly affects the quality of life. It is estimated that it affects 25% of the population although, on many occasions, medical attention is not requested for various reasons such as shame, thinking that it is a normal part of the ageing process, that it has no solution… However, there are now more and more treatments available to cure urinary incontinence, or at least improve the symptoms and quality of life.
We must differentiate between various types of urinary incontinence. It is essential to distinguish between urinary incontinence related to effort and urinary incontinence related to the urge to urinate that cannot be delayed and is usually associated with frequent daytime and night-time micturition. The latter is known as overactive bladder. Each entity will have a specific treatment, as the mechanism is related either to the urinary sphincter and pelvic floor or to the bladder function itself. Sometimes, patients also refer to a vaginal lump, which is a genital prolapse that may be associated with urinary incontinence due to weakness of the pelvic floor.
Among the common risk factors are childbirth, gynaecological surgeries, obesity… The first stages of treatment generally include measures such as weight control, fluid intake adequacy, physical exercises and pelvic floor exercises, individualised according to the patient.
Overactive Bladder

In case of an overactive bladder-urge incontinence, the second step is pharmacological treatment for cases where satisfactory control of symptoms is not achieved. Includes treatments such as the administration of botulinum toxin (BOTOX).
This treatment is applied routinely by the members of the unit in a minimally invasive manner, offering good results regarding symptom control and enabling the interruption of chronic pharmacological treatment.
Overactive bladder syndrome: is characterised by the urgency, with or without urge urinary incontinence, usually with an increased daytime urination frequency and nocturia, and in the absence of infection or any other obvious pathology.
Overactive bladder is classified as neurogenic (NOB) when there is an identified neurological disease, being frequent causes: Parkinson’s, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injuries or strokes, among others. NOB has an overall prevalence of 12-19%, placing an enormous burden on the healthcare system, the society, and the quality of life of the affected individuals. In urology, the use of onabotulinumtoxinA has been widely evaluated in patients with NOB.
- Pharmacological therapy
- Botulinum toxin
The conventional treatment with general measures, bladder training and first-line pharmacological treatment does not always manage to control the symptoms, in addition to abandonment due to side effects, lack of efficacy or being first-line pharmacological treatment contraindicated.
When patients are intolerant or resistant to drug treatment, the application of botulinum toxin offers high efficiency rates in patients where anticholinergics do to work or in those who could not tolerate their adverse effects.
To the improvement of clinical parameters (decrease in incontinence episodes, urgency, urination frequency, etc.), it must be added that of the urodynamic parameters (increase in maximum cystomanometric capacity, reflex volume or volume at first involuntary contraction, maximum detrusor pressure, etc.), with an average duration of the therapeutic effects of 6-12 months.
The procedure is performed under sedation and it does not require hospital admission.
The application of onabotulinumtoxinA significantly improves, not only clinical symptoms, but also urodynamic parameters in patients with OBI who have been inadequately treated with anticholinergics. This is a simple technique, with minimal adverse effects and generally well tolerated.
Neurogenic Bladder

Neurogenic dysfunction of the lower urinary tract or neurogenic bladder is a voiding dysfunction that occurs in patients with pathologies affecting bladder innervation. It appears in patients with neurogenic pathologies such as multiple sclerosis, after strokes, myelomeningoceles, spinal cord injuries, surgeries affecting bladder innervation, etc.
Clinically it can manifest itself with urinary incontinence, micturition failure or urination urge. In addition, if it is not properly managed, it can lead to the existence of urinary tract infections, or even impairment of kidney function.
Diagnosis of the neurogenic dysfunction of the lower urinary tract is performed through a functional study of the bladder-sphincter axis, where the urodynamic study is a fundamental part of determining the type of dysfunction present. In addition, an evaluation by a specialised unit in the lower urinary system dysfunctions is essential to optimise management.
Treatment in case of neurogenic bladder should be individualised according to clinical manifestations with the objective of preserving kidney function, improving quality of life, preventing infections and improving symptoms.
Available treatments include pelvic floor rehabilitation, different pharmacological treatments, self-catheterisation to ensure adequate bladder voiding and avoiding the need for catheterisation, application of botulinum toxin or even reconstructive surgery.
Stress Urinary Incontinence
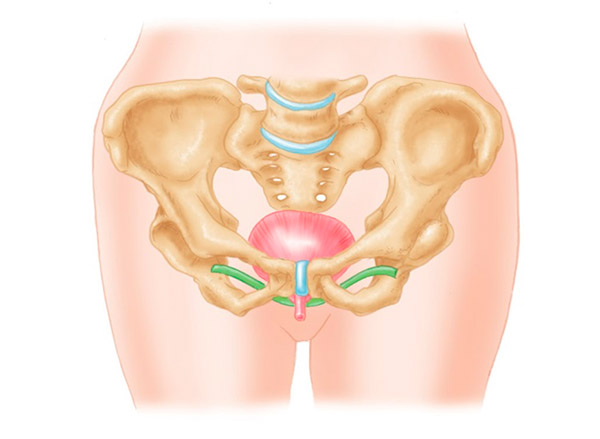
In case of stress urinary incontinence and genital prolapse, surgery is considered to correct pelvic floor disorders.
In our unit we conduct a detailed study of the patient with incontinence and genital prolapse, and we offer diverse treatments and prevention strategies including rehabilitative measures for the pelvic floor along with minimally invasive surgery of the urinary incontinence and correction of pelvic organ prolapse, using the different treatment options with suburethral bands, adjustable slings or artificial urinary sphincter.
Pelvic Pain Syndrome

Pelvic pain is a pathology that requires an approach with specialists in the field, requiring individualised study and treatment. For this purpose, we offer the equipment for a detailed diagnosis and to suggest management including the different strategies available including pharmacological therapy, intravesical instillations and botulinum toxin.
